밑바닥부터 구현해보는 UI라이브러리 만들기1 (상태)
예제링크
npm 링크: https://www.npmjs.com/package/reona
프로젝트 링크: https://github.com/dkpark10/reona
해당 게시글에 관한 링크: https://github.com/dkpark10/reona-track/tree/master/track/01-state
아키텍처 설계#
인터페이스는 react와 동일하게 함수형 컴포넌트로 작성한다. 데이터 상태 변경에 따른 간단한 카운터 예제를 작성해본다.
1import { html, state } from '../core'; 2 3export default function Counter() { 4 const data = state({ 5 count: 0, 6 }); 7 8 const increase = () => { 9 data.count += 1; 10 } 11 12 const decrease = () => { 13 data.count -= 1; 14 } 15 16 return html` 17 <div id="app"> 18 <button type="button" @click=${increase}>increase</button> 19 <button type="button" @click=${decrease}>decrease</button> 20 <div>${data.count}</div> 21 </div> 22 `; 23}
함수형 컴포넌트의 경우 렌더링 시 매번 함수를 호출하기에 해당 컴포넌트의 상태, props, vdom, 라이프 사이클 등
이를 관리해야 할 별도의 인스턴스가 필수적이다. 어찌보면 react class component와 비슷하다 볼 수 있다. 본 프로젝트에서는 이를 ComponentInstance 객체로 구현한다. 아래 이미지는 해당 프로젝트의 전체 구성도이다.
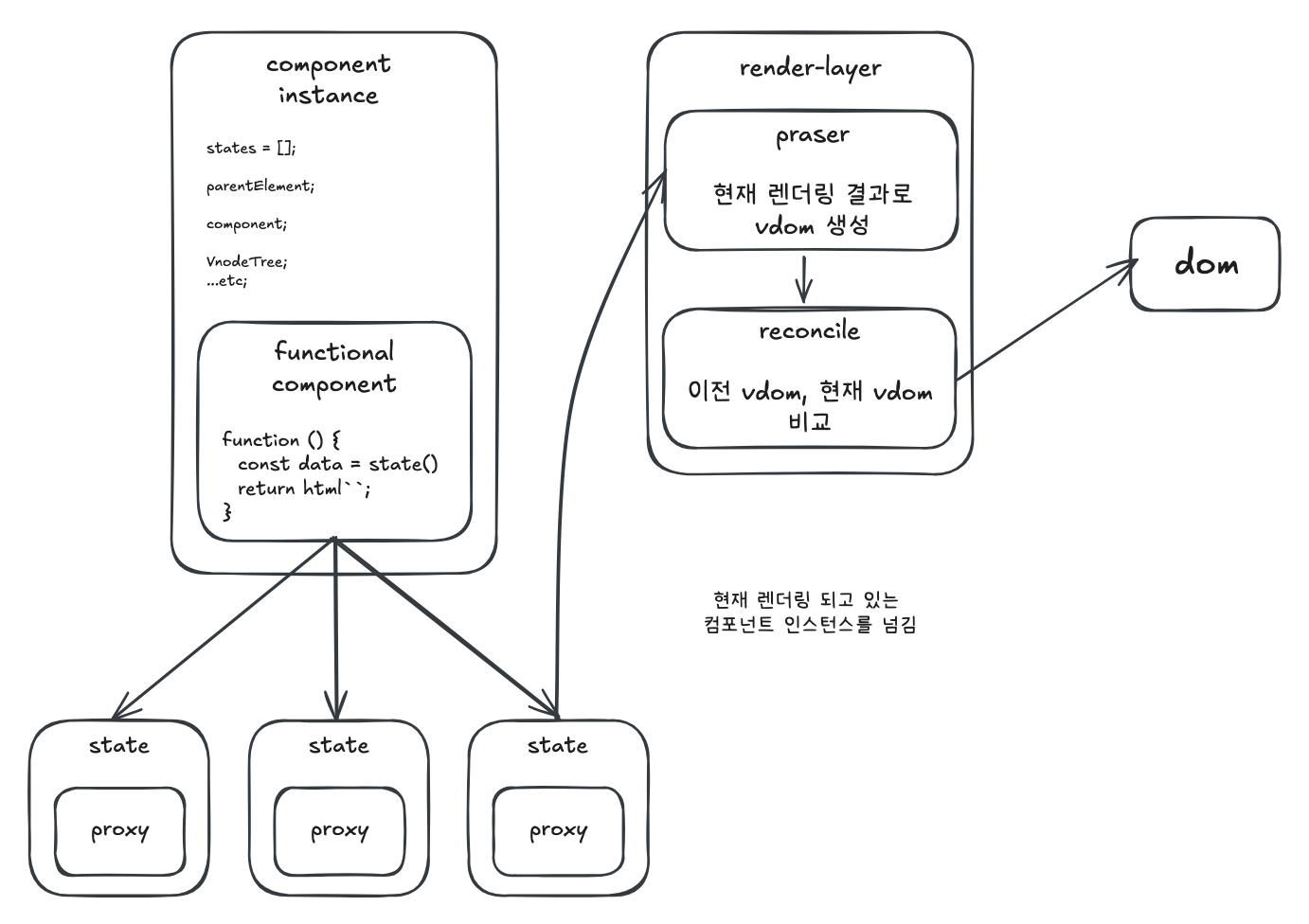
전체 순서#
11. 함수형 컴포넌트를 가지고와 인스턴스를 생성한다. 2 32. 함수형 컴포넌트의 반환값을 가지고 Vdom을 생성한다. 4 53. Vdom을 가지고 실제 dom을 생성한다. 6 74. 실제 dom을 브라우저에 부착한다. 8 95. 상태 업데이트 시 이전 Vdom과 현재 VDom을 가지고 비교하여 실제 dom을 업데이트 한다.
컴포넌트가 실제 dom에 반영되려면 루트 엘리먼트로부터 컴포넌트가 부착되어야 한다. 루트 엘리먼트와 해당 컴포넌트를 rootRender 함수에 넘긴다.
1rootRender(document.getElementById('root'), Counter);
runtime-dom.js
1// 부착할 엘리먼트와 함수형 컴포넌트를 파라미터로 넘김 2function rootRender( 3 container, 4 component, 5) { 6 const instance = new ComponentInstance(component, 0); // 컴포넌트를 관리할 인스턴스 생성 7 instance.render(container); 8 return instance; 9}
ComponentInstance를 생성하기 위한 생성자 옵션으로 컴포넌트 함수와 html 트리에서의 고유 위치 넘버링을 넘긴다. 루트 엘리먼트에 첫 부착되므로 0으로 넘긴다. 함수 컴포넌트 반환값의 경우 html 함수와 함께 렌더링할 선언적 dom 데이터를 넘겨주는데 html 함수는 문자열과 동적인 값을 넘겨주고 marker를 표시한채 그대로 넘긴다.
이는 웹 컴포넌트 기반 라이브러리 lit에서 컨셉을 차용했다.
즉 html 함수의 역할은 추후 가상돔을 생성할 때 문자열에 표시된 marker에 동적값을 주입할 문자열 템플릿을 반환하는 것이다.
1function html(strings, ...values) { 2 let idx = 0; 3 const rawString = strings 4 .join('%%identifier%%') 5 .replace(/%%identifier%%/g, () => `__marker_${idx++}__`); 6 7 return { template: rawString, values }; 8}
html 함수의 반환 값
1html` 2 <div id="app"> 3 <button type="button" @click=${increase}>increase</button> 4 <button type="button" @click=${decrease}>decrease</button> 5 <div>${data.count}</div> 6 </div> 7`; 8 9// 결과 10 11{ 12 template: 13 <div id="app"> 14 <button type="button" data-testid="increase" @click=__marker_0__>increase</button> 15 <button type="button" data-testid="decrease" @click=__marker_1__>decrease</button> 16 <div id="value">__marker_2__</div> 17 </div>, 18 19 values: [f, f, 0], 20}
컴포넌트 인스턴스#
함수형 컴포넌트를 관리할 컴포넌트 인스턴스를 만든다. 인스턴스가 하는일은 다음과 같다.
11. 함수형 컴포넌트 원본과 상태를 보관 22. 렌더링 시 현재 인스턴스를 전역에 할당 (훅이 접근할 수 있도록) 33. VNode 생성 → 실제 DOM 생성 → 부모에 삽입 44. 리렌더링 시 새 DOM으로 교체
component-instance.js
1export default class ComponentInstance { 2 states = []; // 상태를 관리할 훅 배열 3 parentElement; // DOM이 삽입될 부모 엘리먼트 4 component; // 함수형 컴포넌트 원본 5 prevVnodeTree; // 이전 렌더링의 VNode 6 nextVnodeTree; // 현재 렌더링의 VNode 7 currentDom; // 실제 마운트된 DOM 8 sequence; // 트리에서의 위치 (전위순회 기준) 9 hookIndex = 0; // 훅 포인터 (마운트 전) 10 hookLimit = 0; // 훅 최대 개수 (마운트 후 고정) 11 stateHookIndex = 0; // 상태 훅 포인터 12 isMounted = false; // 마운트 여부 13 14 constructor(component, options) { 15 this.component = component; 16 this.sequence = options.sequence; 17 } 18}
render 메서드 - 초기 마운트
컴포넌트를 처음 DOM에 부착할 때 호출된다.
1render(parentElement, isRerender) { 2 if (isRerender) { 3 this.stateHookIndex = 0; 4 } 5 6 // 1. 현재 렌더링 중인 인스턴스를 전역에 할당 7 currentInstance = this; 8 9 // 2. 컴포넌트 함수 실행 → 템플릿 반환 10 const template = this.component(); 11 12 this.parentElement = parentElement; 13 14 // 3. 템플릿 → VNode 트리로 파싱 15 this.prevVnodeTree = parse(template, this.sequence + 1); 16 17 // 4. VNode → 실제 DOM 생성 18 this.currentDom = createDOM(this.prevVnodeTree, parentElement); 19 20 // 5. 부모에 DOM 삽입 21 parentElement.insertBefore(this.currentDom, null); 22 this.isMounted = true; 23}
reRender 메서드 - 상태 변경 시 재렌더링
상태가 변경되면 호출되어 DOM을 교체한다.
1reRender() { 2 this.stateHookIndex = 0; 3 4 // 1. 현재 렌더링 중인 인스턴스를 전역에 할당 5 currentInstance = this; 6 7 // 2. 컴포넌트 함수 재실행 8 const template = this.component(); 9 10 // 3. 새로운 VNode 트리 생성 11 this.nextVnodeTree = parse(template, this.sequence + 1); 12 13 // 4. 새 DOM 생성 14 const newDom = createDOM(this.nextVnodeTree, this.parentElement); 15 16 // 5. 기존 DOM을 새 DOM으로 일괄 교체 17 this.currentDom.replaceWith(newDom); 18 19 // 6. 참조 업데이트 20 this.currentDom = newDom; 21 this.prevVnodeTree = this.nextVnodeTree; 22}
핵심: currentInstance 전역 할당#
여기서 가장 중요한 로직은 현재 렌더링 중인 인스턴스를 전역에 할당하는 것이다. 이를 통해 훅 함수 내부 실행 시 현재 렌더링 진행중인 컴포넌트를 확인할 수 있다.
1currentInstance = this; 2const template = this.component();
React 역시 렌더링 중인 Fiber 정보를 전역 변수에 등록하여 훅이 현재 실행 중인 컴포넌트를 추적한다.
hook 로직 작성하기#
state 훅이 하는 일은 다음과 같다.
11. 현재 렌더링 중인 인스턴스 가져오기 (어떤 컴포넌트에서 호출되었는지 파악) 22. 훅 유효성 검사 (조건부 호출 방지) 33. 리렌더링 시 이전 상태값 반환 (초기값이 아닌 저장된 값) 44. Proxy로 반응형 상태 생성 (값 변경 시 자동 리렌더링)
Proxy vue의 반응성 컨셉을 사용하였으며 구현 단순화를 위해 Proxy 기반 반응성을 사용한다.
1단계: 현재 인스턴스 가져오기#
컴포넌트 함수 실행 전에 전역에 할당된 currentInstance를 가져온다. 이것이 React에서 훅이 컴포넌트 내부에서만 호출되어야 하는 이유다.
hooks.js
1import { getCurrentInstance } from './component-instance'; 2 3function checkInvalidHook(currentInstance) { 4 if (currentInstance.isMounted && currentInstance.hookIndex > currentInstance.hookLimit) { 5 throw new Error('훅은 함수 최상단에 선언해야 합니다.'); 6 } 7 8 if (!currentInstance.isMounted) { 9 currentInstance.hookIndex += 1; 10 } 11} 12 13export function state(initial) { 14 const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance(); 15 16 // 컴포넌트 외부에서 호출하면 에러 17 if (currentInstance === null) { 18 throw new Error('state 함수는 컴포넌트 내에서 선언해야 합니다.'); 19 } 20 // ...생략 21}
2단계: 훅 유효성 검사#
마운트 시점에 훅 개수를 기록해두고, 리렌더링 시 그 개수를 초과하면 에러를 던진다.
이것이 실제 react에서도 훅을 조건부로 호출할 수 없는 이유다.
1function checkInvalidHook(currentInstance) { 2 // 마운트 후 훅 개수가 늘어나면 에러 3 if (currentInstance.isMounted && currentInstance.hookIndex > currentInstance.hookLimit) { 4 throw new Error('훅은 함수 최상단에 선언해야 합니다.'); 5 } 6 7 // 마운트 전에는 훅 포인터 증가 8 if (!currentInstance.isMounted) { 9 currentInstance.hookIndex += 1; 10 } 11}
3단계: 이전 상태값 반환#
매 렌더링마다 state()가 호출되지만, 초기값이 아닌 이전에 저장된 상태를 반환해야 한다. stateHookIndex를 포인터로 사용해 states 배열에서 해당 순서의 상태를 가져온다.
1const stateIndex = currentInstance.stateHookIndex++; 2 3// 이미 상태가 있으면 그대로 반환 (리렌더링 시) 4if (currentInstance.states[stateIndex] !== undefined) { 5 return currentInstance.states[stateIndex]; 6}
4단계: Proxy로 반응형 상태 생성#
초기 마운트 시에만 실행된다. Proxy의 set trap을 활용해 값 변경 시 자동으로 리렌더링을 트리거한다.
1const data = new Proxy(initial, { 2 get(target, key, receiver) { 3 return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver); 4 }, 5 6 set(target, key, value, receiver) { 7 const prevValue = Reflect.get(receiver, key); 8 const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver); 9 10 // 값이 변경되면 리렌더링 11 if (prevValue !== value) { 12 currentInstance.reRender(); 13 } 14 return result; 15 }, 16}); 17 18// 인스턴스의 states 배열에 저장 19currentInstance.states[stateIndex] = data; 20return data;
훅 포인터가 동작하는 방식#
아래와 같이 훅이 여러 개 있을 때 인스턴스 변수들이 어떻게 동작하는지 살펴보자.
1function Component() { 2 const data1 = state({ foo: 1 }); // stateIndex = 0 3 const data2 = state({ bar: 1 }); // stateIndex = 1 4 return ... 5}
마운트 이전
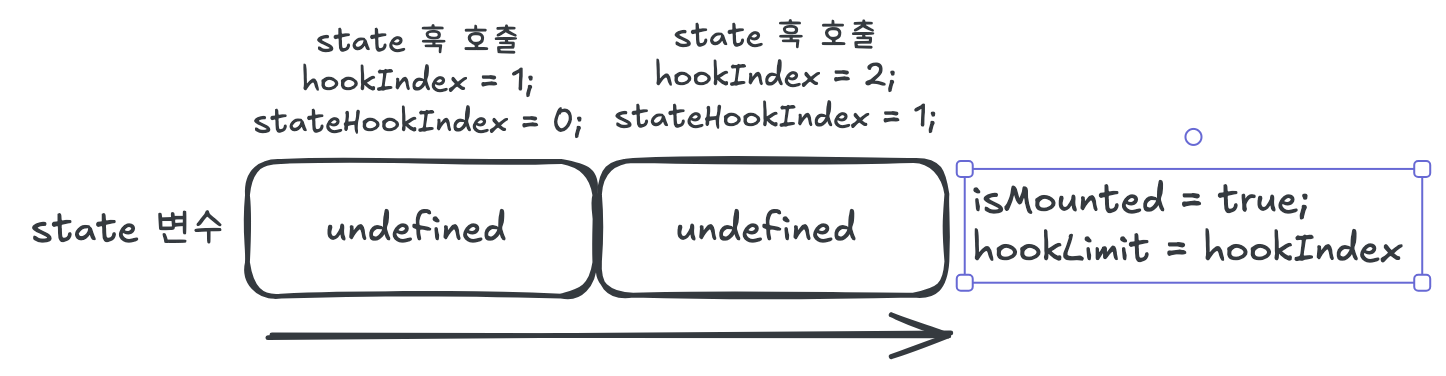
마운트 이전에는 훅을 순회하면서 포인터를 증가시키고, states 배열에 초기값을 세팅한다.
마운트 완료 후 hookLimit에 훅 개수를 저장하여 이후 추가 훅 호출을 방지한다.
마운트 이후 리렌더링
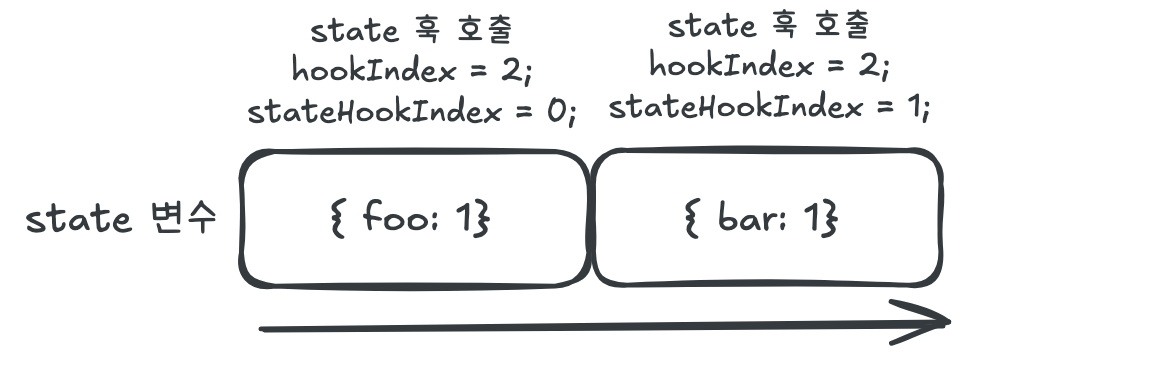
리렌더링 시에는 states 배열에 값이 이미 존재하므로 저장된 상태를 그대로 반환한다.
재조정 및 이벤트, 데이터 바인딩을 위한 Vdom 생성#
앞서 html 함수에서 받은 결과물을 이제 실제로 dom에 부착해야 하는 작업이 남았다. Vdom을 생성하는 parser를 작성한다.
파서의 전체 흐름#
파서가 하는 일을 단계별로 요약하면 다음과 같다.
11. template 문자열 → DOM으로 파싱 (브라우저 template 엘리먼트 활용) 22. DOM 노드 순회하면서 VNode로 변환 (convertNode, convertChild) 33. \_\_marker_N\_\_ 을 만나면 values 배열에서 실제 값으로 치환 44. 최종 VNode 트리 반환
marker 치환 과정 예시
1// 입력 2html`<button @click=${onClick}>${count}개</button>` 3 4// 1. html 함수 결과 5{ 6 template: '<button @click=__marker_0__>__marker_1__개</button>', 7 values: [onClick, 5] 8} 9 10// 2. parse 결과 (VNode) 11{ 12 type: 'element', 13 tag: 'button', 14 attr: { '@click': onClick }, // marker_0 → onClick 함수 15 children: [ 16 { type: 'text', value: '5개' } // marker_1 → 5 17 ] 18}
1단계: 템플릿을 DOM으로 변환#
html 함수에서 받은 template 문자열을 브라우저의 template 엘리먼트를 활용해 파싱한다. template 엘리먼트는 innerHTML에 문자열을 넣으면 자동으로 DOM 트리를 생성해준다.
parser.js
1export default function parse(renderResult) { 2 const { template: t } = renderResult; 3 const template = document.createElement('template'); 4 5 template.innerHTML = t.trim(); 6 7 // 루트 엘리먼트는 1개여야 한다 8 if (template.content.childNodes.length > 1) { 9 throw new Error('루트 엘리먼트는 1개여야 합니다.'); 10 } 11 12 const firstChild = template.content.firstChild; 13 14 // 텍스트 노드라면 15 if (firstChild && firstChild.nodeType === Node.TEXT_NODE) { 16 return convertChild(firstChild); 17 } 18 19 return convertNode(template.content.firstElementChild); 20}
2단계: 엘리먼트 노드 변환 (convertNode)#
엘리먼트 노드를 VNode로 변환한다. 속성(attributes)을 순회하며 marker가 있으면 values 배열에서 실제 값을 가져온다.
1let valueIndex = 0; 2 3function convertNode(el) { 4 if (!el) { 5 return { type: 'text', value: '' }; 6 } 7 8 const attrs = {}; 9 for (const attr of el.attributes) { 10 const { values } = renderResult; 11 12 // marker 패턴 매칭 13 const markers = attr.value.match(/__marker_(\d+)__/g); 14 if (markers && markers.length >= 1) { 15 // 함수면 이벤트 핸들러로 할당 16 if (typeof values[valueIndex] === 'function') { 17 attrs[attr.name] = values[valueIndex++]; 18 // 객체면 경고와 함께 할당 19 } else if (typeof values[valueIndex] === 'object') { 20 attrs[attr.name] = values[valueIndex++]; 21 // 원시값이면 문자열로 치환 22 } else { 23 attrs[attr.name] = attr.value.replace(/__marker_(\d+)__/g, () => { 24 const v = values[valueIndex++]; 25 return v !== undefined ? String(v) : ''; 26 }); 27 } 28 } else { 29 // marker가 없으면 그대로 할당 30 attrs[attr.name] = attr.value; 31 } 32 } 33 34 // 자식 노드들을 재귀적으로 변환 35 const children = []; 36 for (const child of el.childNodes) { 37 const vnode = convertChild(child); 38 if (vnode) { 39 children.push(vnode); 40 } 41 } 42 43 return { 44 type: 'element', 45 tag: el.tagName.toLowerCase(), 46 children, 47 attr: attrs, 48 }; 49}
3단계: 텍스트/자식 노드 변환 (convertChild)#
텍스트 노드를 처리하고, marker가 있다면 실제 값으로 치환한다. 값이 또 다른 컴포넌트(renderResult 객체)라면 재귀적으로 parse를 호출한다.
1function convertChild(node) { 2 // 텍스트 노드 처리 3 if (node.nodeType === Node.TEXT_NODE) { 4 let text = node.textContent ?? ''; 5 if (/^\s*$/.test(text)) return null; // 공백만 있으면 무시 6 7 const markers = text.match(/__marker_(\d+)__/g); 8 if (markers && markers.length >= 1) { 9 return markers.map(() => { 10 const { values } = renderResult; 11 const value = values[valueIndex]; 12 13 // 값이 컴포넌트라면 재귀 파싱 14 if (isRenderResultObject(value)) { 15 return parse(value); 16 } 17 18 // 배열이면 각각 파싱 19 if (Array.isArray(value)) { 20 return values[valueIndex++].map((v) => { 21 if (isRenderResultObject(v)) { 22 return parse(v); 23 } 24 }); 25 } 26 27 // 일반 값이면 텍스트로 치환 28 text = replaceMarkers(text); 29 return { type: 'text', value: text }; 30 }); 31 } 32 33 return { type: 'text', value: text }; 34 } 35 36 // 엘리먼트 노드면 convertNode로 위임 37 if (node.nodeType === Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { 38 return convertNode(node); 39 } 40 41 return null; 42}
파싱 결과 예시
1const template = html`<div id="app" @click=${onClick}>${text}</div>`; 2const result = parse(template); 3 4// result 5{ 6 type: 'element', 7 tag: 'div', 8 children: [ { type: 'text', value: 'text' } ], 9 attr: { id: 'app', '@click': [Function: onClick] } 10}
VNode를 실제 DOM으로 변환#
파싱된 VNode 트리를 실제 브라우저 DOM으로 변환한다.
createDOM이 하는 일#
- 텍스트 노드면 →
로 생성1document.createTextNode() - 엘리먼트 노드면 →
로 생성1document.createElement() - 속성 처리 →
같은 이벤트는1@click
, 나머지는1addEventListener1setAttribute - 자식 노드 재귀 처리 → children을 순회하며 createDOM 재귀 호출
runtime-dom.js
1export function createDOM(vnode, parentElement) { 2 // 1. 텍스트 노드 처리 3 if (vnode.type === 'text') { 4 return document.createTextNode(vnode.value); 5 } 6 7 // 2. 엘리먼트 생성 8 const el = document.createElement(vnode.tag); 9 10 // 3. 속성 처리 11 if (vnode.attr) { 12 for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(vnode.attr)) { 13 // @click 같은 이벤트 바인딩 14 if (/@([^\s=/>]+)/.test(key) && typeof value === 'function') { 15 const eventName = key.slice(1); 16 el.addEventListener(eventName, value); 17 } else { 18 el.setAttribute(key, value); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 23 // 4. 자식 노드 재귀 처리 24 vnode.children?.forEach((child) => { 25 const c = createDOM(child, el); 26 if (c) { 27 el.appendChild(c); 28 } 29 }); 30 31 return el; 32}
DOM 삽입과 교체#
생성한 DOM은 초기 렌더링 시 부모에 삽입하고, 리렌더링 시 기존 DOM을 교체한다.
1// 초기 렌더링: 부모에 삽입 2this.currentDom = createDOM(this.prevVnodeTree, this.parentElement); 3this.parentElement.insertBefore(this.currentDom, null); 4 5// 리렌더링: 기존 DOM을 새 DOM으로 일괄 교체 6const newDom = createDOM(this.nextVnodeTree, this.parentElement); 7this.currentDom.replaceWith(newDom);
렌더링 최적화#
현재 Proxy의 set trap은 속성이 변경될 때마다 리렌더링을 트리거한다. 여러 속성을 동시에 변경하면 그 횟수만큼 리렌더링이 발생한다.
1const data = state({ a: 0, b: 0 }); 2 3const trigger = () => { 4 data.a += 1; // 리렌더링 1번 5 data.b += 1; // 리렌더링 2번 → 비효율! 6}
requestAnimationFrame으로 배치 처리#
대부분의 디스플레이 디바이스는 60Hz 주사율을 사용하므로 1프레임(약 16ms) 안에 발생한 모든 상태 변경을 모아서 한 번만 렌더링하면 된다.
requestAnimationFrame은 다음 프레임 직전에 콜백을 실행하므로, 같은 프레임 내의 여러 업데이트를 배치로 처리할 수 있다.
배치 업데이트 흐름
1data.a += 1 → 큐에 인스턴스 추가, RAF 예약 2data.b += 1 → 이미 큐에 있음, 무시 3───────────────────────────────────────── 4 ↓ (다음 프레임) 5 6RAF 콜백 실행 → 큐의 인스턴스들 한 번씩 리렌더링
update 함수 구현
1const renderQueue = new Set(); // 중복 방지를 위해 Set 사용 2let rafId = null; 3 4export function update(instance) { 5 // 1. 렌더링할 인스턴스를 큐에 추가 6 renderQueue.add(instance); 7 8 // 2. 이미 RAF가 예약되어 있으면 추가 예약 안 함 9 if (rafId !== null) return; 10 11 // 3. 다음 프레임에 배치 렌더링 예약 12 rafId = requestAnimationFrame(() => { 13 try { 14 // 큐에 있는 모든 인스턴스 렌더링 15 renderQueue.forEach((instance) => { 16 instance.reRender(); 17 }); 18 } finally { 19 // 정리 20 renderQueue.clear(); 21 rafId = null; 22 } 23 }); 24}
Proxy set trap에 적용
기존의 reRender() 직접 호출을 update() 함수로 교체한다.
1set(target, key, value, receiver) { 2 const prevValue = Reflect.get(receiver, key); 3 const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver); 4 5 if (prevValue !== value) { 6 // reRender() 대신 update()로 배치 처리 7 update(currentInstance); 8 } 9 return result; 10}
이제 같은 프레임 내에서 아무리 많은 상태를 변경해도 1번만 리렌더링된다.
전체 파일#
index.js
1import { state } from './hooks' 2 3/** 4 * @param {string[]} strings 5 * @param {any[]} values 6 */ 7function html(strings, ...values) { 8 let idx = 0; 9 const rawString = strings 10 .join('%%identifier%%') 11 .replace(/%%identifier%%/g, () => `__marker_${idx++}__`); 12 13 return { template: rawString, values }; 14} 15 16export { 17 state, html 18};
hooks.js
1import { getCurrentInstance } from './component-instance'; 2 3const renderQueue = new Set(); 4let rafId = null; 5 6export function update(instance) { 7 renderQueue.add(instance); 8 9 if (rafId !== null) return; 10 11 rafId = requestAnimationFrame(() => { 12 try { 13 renderQueue.forEach((instance) => { 14 instance.reRender(); 15 }); 16 } finally { 17 renderQueue.clear(); 18 rafId = null; 19 } 20 }); 21} 22 23function isPrimitive(value) { 24 return value === null || (typeof value !== 'object' && typeof value !== 'function'); 25} 26 27function checkInvalidHook(currentInstance) { 28 if (currentInstance.isMounted && currentInstance.hookIndex > currentInstance.hookLimit) { 29 throw new Error('훅은 함수 최상단에 선언해야 합니다.'); 30 } 31 32 if (!currentInstance.isMounted) { 33 currentInstance.hookIndex += 1; 34 } 35} 36 37export function state(initial) { 38 const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance(); 39 if (currentInstance === null) { 40 throw new Error('state 함수는 컴포넌트 내에서 선언해야 합니다.'); 41 } 42 43 checkInvalidHook(currentInstance); 44 45 const stateIndex = currentInstance.stateHookIndex++; 46 if (currentInstance.states[stateIndex] !== undefined) { 47 return currentInstance.states[stateIndex]; 48 } 49 50 if (initial && isPrimitive(initial)) { 51 throw new Error('원시객체 입니다. 객체 형식으로 넣으세요.'); 52 } 53 54 const data = new Proxy(initial, { 55 get(target, key, receiver) { 56 return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver); 57 }, 58 59 set(target, key, value, receiver) { 60 const prevValue = Reflect.get(receiver, key); 61 62 const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver); 63 if (prevValue !== value) { 64 update(currentInstance); 65 } 66 return result; 67 }, 68 }); 69 currentInstance.states[stateIndex] = data; 70 return data; 71}
component-instance.js
1import parse from './parser'; 2import { createDOM } from './runtime-dom'; 3 4/** @description 현재 렌더링 되고 있는 컴포넌트 */ 5let currentInstance = null; 6export function getCurrentInstance() { 7 return currentInstance; 8} 9 10/** @description 컴포넌트 인스턴스 - 상태, Props, 생명주기, VNode 트리, DOM 참조를 관리 */ 11export default class ComponentInstance { 12 /** @type {Array<unknown>} */ 13 states = []; 14 15 /** @type {HTMLElement | null} */ 16 parentElement; 17 18 /** @type {Function} */ 19 component; 20 21 /** @type {Object | null} */ 22 prevVnodeTree; 23 24 /** @type {Object | null} */ 25 nextVnodeTree; 26 27 /** @type {HTMLElement | null} */ 28 currentDom; 29 30 /** @type {Number} html 트리에서의 위치 */ 31 sequence; 32 33 hookIndex = 0; 34 35 hookLimit = 0; 36 37 stateHookIndex = 0; 38 39 isMounted = false; 40 41 constructor(component, options) { 42 this.component = component; 43 this.sequence = options.sequence; 44 } 45 46 hookIndexInitialize() { 47 this.stateHookIndex = 0; 48 } 49 50 render(parentElement, isRerender) { 51 // 부모 리렌더링으로 인한 자식 리렌더링이라면 52 if (isRerender) { 53 this.hookIndexInitialize(); 54 } 55 56 /** @description 현재 렌더링 되고 있는 컴포넌트를 할당 */ 57 currentInstance = this; 58 const template = this.component(); 59 60 this.parentElement = parentElement; 61 this.prevVnodeTree = parse(template, this.sequence + 1); 62 63 this.currentDom = createDOM(this.prevVnodeTree, parentElement); 64 parentElement.insertBefore(this.currentDom, null); 65 this.isMounted = true; 66 this.hookLimit = this.hookIndex; 67 } 68 69 reRender() { 70 this.hookIndexInitialize(); 71 currentInstance = this; 72 const template = this.component(); 73 74 this.nextVnodeTree = parse(template, this.sequence + 1); 75 76 const newDom = createDOM(this.nextVnodeTree, this.parentElement); 77 this.currentDom.replaceWith(newDom); 78 79 // 새로운 값들을 이전 변수에 할당 80 this.currentDom = newDom; 81 this.prevVnodeTree = this.nextVnodeTree; 82 } 83} 84
parser.js
1import ComponentInstance from './component-instance'; 2 3/** 4 * @typedef {Object} RenderResult 5 * @property {string} template 6 * @property {any[]} values 7 */ 8 9/** 10 * @param {RenderResult} obj 11 * @returns {boolean} 12 */ 13function isRenderResultObject(obj) { 14 return ( 15 obj !== null && 16 typeof obj === 'object' && 17 typeof obj.template === 'string' && 18 Array.isArray(obj.values) 19 ); 20} 21 22/** 23 * @param {Object} obj 24 * @returns {boolean} 25 */ 26export function isEmpty(obj) { 27 return Object.keys(obj).length <= 0; 28} 29 30/** 31 * @typedef {Object} VTextNode 32 * @property {"text"} type 33 * @property {string} value 34 * @export 35 */ 36 37/** 38 * @typedef {Object} VElementNode 39 * @property {"element"} type 40 * @property {keyof HTMLElementTagNameMap} tag 41 * @property {Props=} attr 42 * @property {VNode[]} children 43 * @export 44 */ 45 46/** 47 * @typedef {Object} VComponent 48 * @property {"component"} type 49 * @property {ComponentInstance} instance 50 * @export 51 */ 52 53/** 54 * @typedef {VTextNode | VElementNode | VComponent} VNode 55 * @export 56 */ 57 58/** 59 * @description 받은 html을 vnode tree로 만듬 60 * @param {RenderResult} renderResult 61 * @param {number} sequence 62 * @returns {VNode} 63 */ 64export default function parse(renderResult) { 65 let valueIndex = 0; 66 67 /** 68 * @param {HTMLElement} el 69 */ 70 function convertNode(el) { 71 if (!el) { 72 return { 73 type: 'text', 74 value: '', 75 }; 76 } 77 78 const attrs = {}; 79 80 for (const attr of el.attributes) { 81 const { values } = renderResult; 82 83 const nameMarker = attr.name.match(/^__marker_(\d+)__$/); 84 if (nameMarker) { 85 const value = values[valueIndex++]; 86 if (value && typeof value === 'string') { 87 attrs[value] = true; 88 } 89 continue; 90 } 91 92 const markers = attr.value.match(/__marker_(\d+)__/g); 93 if (markers && markers.length >= 1) { 94 if (typeof values[valueIndex] === 'function') { 95 attrs[attr.name] = values[valueIndex++]; 96 } else if (typeof values[valueIndex] === 'object') { 97 attrs[attr.name] = values[valueIndex++]; 98 console.warn( 99 `${el.tagName.toLowerCase()} 엘리먼트에 ${attr.name} 속성에 ${values[valueIndex - 1]} 객체가 들어가 있습니다. 값이 맞는지 확인하세요.` 100 ); 101 } else { 102 attrs[attr.name] = attr.value.replace(/__marker_(\d+)__/g, () => { 103 const v = values[valueIndex++]; 104 return v !== undefined ? String(v) : ''; 105 }); 106 } 107 } else { 108 attrs[attr.name] = attr.value; 109 } 110 } 111 112 const children = []; 113 for (const child of el.childNodes) { 114 const vnode = convertChild(child); 115 if (vnode) { 116 if (Array.isArray(vnode)) { 117 const filteredEmptyTextValue = vnode.filter((node) => !!node).flat(); 118 children.push(...filteredEmptyTextValue); 119 } else { 120 children.push(vnode); 121 } 122 } 123 } 124 125 return { 126 type: 'element', 127 tag: el.tagName.toLowerCase(), 128 children, 129 ...(!isEmpty(attrs) && { attr: attrs }), 130 }; 131 } 132 133 /** 134 * @param {ChildNode} node 135 */ 136 function convertChild(node) { 137 if (node.nodeType === Node.TEXT_NODE) { 138 let text = node.textContent ?? ''; 139 140 // 공백을 제거 141 if (/^\s*$/.test(text)) return null; 142 143 // marker가 붙어있는 경우가 있으므로 match 144 const markers = text.match(/__marker_(\d+)__/g); 145 if (markers && markers.length >= 1) { 146 return markers.map(() => { 147 const { values } = renderResult; 148 const value = values[valueIndex]; 149 150 if (isRenderResultObject(value)) { 151 const vdom = parse(value); 152 return vdom; 153 } 154 155 // 배열이 들어 왔다면 156 if (Array.isArray(value)) { 157 const result = values[valueIndex++].map((value) => { 158 if (isRenderResultObject(value)) { 159 const vdom = parse(value); 160 return vdom; 161 } 162 }); 163 return result; 164 } 165 166 // marker가 있다면 원본 텍스트를 변경한다. 167 if (/__marker_(\d+)__/.test(text)) { 168 text = replaceMarkers(text); 169 return { 170 type: 'text', 171 value: text, 172 }; 173 } 174 // marker 가 없으면 빈 텍스트 반환 175 return null; 176 }); 177 } 178 179 return { 180 type: 'text', 181 value: text, 182 }; 183 } 184 185 if (node.nodeType === Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { 186 return convertNode(node); 187 } 188 189 return null; 190 } 191 192 /** 193 * @param {string} str 194 * @return {string} 195 */ 196 function replaceMarkers(str) { 197 const { values } = renderResult; 198 return str.replace(/__marker_(\d+)__/g, () => { 199 const v = values[valueIndex++]; 200 return v !== undefined ? String(v) : ''; 201 }); 202 } 203 204 // 메인 파싱 로직 205 const { template: t } = renderResult; 206 const template = document.createElement('template'); 207 208 template.innerHTML = t.trim(); 209 210 if (template.content.childNodes.length > 1) { 211 throw new Error('루트 엘리먼트는 1개여야 합니다.'); 212 } 213 214 const firstChild = template.content.firstChild; 215 216 /** 217 * 텍스트 노드, 단일 컴포넌트 처리 218 * html`text`, html`<component />` 219 */ 220 if (firstChild && firstChild.nodeType === Node.TEXT_NODE) { 221 const vDom = convertChild(firstChild); 222 if (Array.isArray(vDom)) { 223 return vDom.filter((v) => !!v)[0]; 224 } 225 return vDom; 226 } 227 228 return convertNode(template.content.firstElementChild); 229}
runtime-dom.js
1import ComponentInstance from "./component-instance"; 2 3export function rootRender( 4 container, 5 component, 6) { 7 if (!component) { 8 throw new Error('컴포넌트가 없습니다.'); 9 } 10 11 const instance = new ComponentInstance(component, 0); 12 instance.render(container); 13 return instance; 14} 15 16export function createDOM(vnode, parentElement) { 17 if (vnode.type === 'text') { 18 return document.createTextNode(vnode.value); 19 } 20 21 const el = document.createElement(vnode.tag); 22 if (vnode.attr) { 23 for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(vnode.attr)) { 24 if (/@([^\s=/>]+)/.test(key) && typeof value === 'function') { 25 const eventName = key.slice(1); 26 el.addEventListener(eventName, value); 27 } else { 28 el.setAttribute(key, value); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 33 vnode.children?.forEach((child) => { 34 const c = createDOM(child, el); 35 if (c) { 36 el.appendChild(c); 37 } 38 }); 39 40 return el; 41}